The Password Problem
Although far from perfect, passwords are still the main way people authenticate themselves to online services. There are a few built in and serious issues with password security, namely:
- People tend to re-use passwords
- Users don’t like to remember long and complex passwords
- People tend not to change passwords frequently (unless forced)
- Criminals are able to hack poorly protected infrastructure to steal credentials and recover plain text details.
Despite this, passwords still dominate the security landscape outside the financial industry.
Brute force attacks explained
Hackers who steal credentials from a service provider, face the task to decode the stored passwords they have stolen. These are almost always stored as encrypted versions of the username and password. The encryption is mathematically irreversible. For years, this was deemed the gold standard and proof against hackers. Over the years however, compute power has grown exponentially, meaning that previously unimaginable quantities of calculations can be performed.
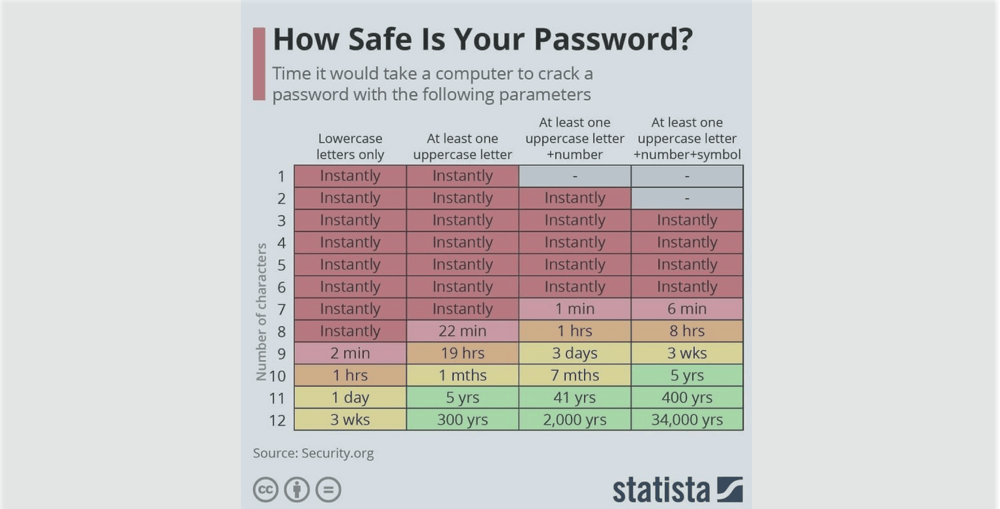
In a brute force attack, a hacker will setup compute resource to effectively try millions of permutations of passwords to recalculate the encrypted credential, until they find a match to the encrypted credential they have stolen. Lists of popular passwords to seed the search can greatly speed the process. As can be seen from the graphic above, even a 10 character lower case password, can be cracked in an hour.
Password Tricks to avoid cracking
For high level password security, passwords should be 11 characters or more, definitely contain a number and ideally a symbol too, such as !?#%.
Don’t use personal information, such as birthday or street address in a password, hackers may have also gained access to that.
Use the “Three words” method. In this you think of three words that you can remember. For example BreadCheeseCat! or AppleBookGlasses? This technique generally results in a long password that is almost un-crackable with current processing power.
Multi-Factor-Authentication “MFA”
If a business offers MFA, you should always try to use it. This involves a secondary method of authentication, such as a code sent via SMS, or the use of a dedicated app or device to generate a code. This is now the gold standard, it is not 100% secure (almost nothing is), but for most users, it is good enough.
Cyber Security email list
If you have a product or service to promote in the cyber security space, please take a look at our Cyber Security Skills page and also our security related job titles page.
Let us know how we can help you, just don’t ask why all cyber-criminals appear to wear hoodies!